1101 W. Sanilac Rd. Caro, MI 48723
989.673.6690
Laser welding technology has gained traction in various industries. Reports indicate that the global laser welding market is projected to reach $4.8 billion by 2027, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 5.6%. The laser welding gun is a critical tool in this evolution. It offers precision and efficiency that traditional welding cannot match.
In the automotive industry, for instance, manufacturers utilize laser welding for its speed and accuracy. This technique minimizes heat distortion, ensuring better quality in joints. However, some challenges exist. High initial costs can deter small businesses from investing in laser welding systems. Furthermore, training personnel to handle these advanced tools poses a significant hurdle.
The versatility of the laser welding gun is noteworthy. It can weld various materials, including metals and plastics. Yet, its full potential is often untapped due to a lack of knowledge. Continuous improvement and innovation are necessary for maximizing its applications in diverse sectors. As the technology evolves, so too must the understanding and skills of the workforce.
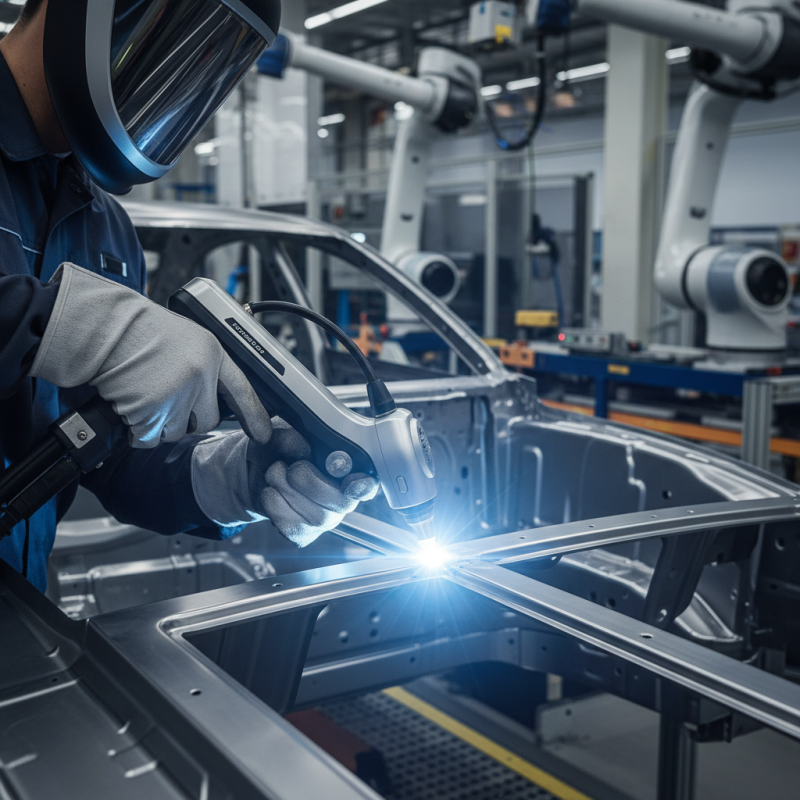

A laser welding gun is a powerful tool used to join materials with high precision. This technology leverages concentrated beams of light to melt and fuse metals. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the laser welding market is expected to reach $21.5 billion by 2026, indicating its growing importance in various industries.
In operation, the laser welding gun generates a laser beam that targets a specific area. This focused energy creates heat, allowing the materials to melt and bond together. The efficiency and speed are remarkable. For example, laser welding can reduce processing times by up to 30%. This technology is especially useful in automotive and aerospace applications, where precision is critical.
However, challenges exist. The high cost of equipment can deter smaller manufacturers. Furthermore, operators require extensive training to use laser welding guns safely and effectively. Despite these hurdles, the advantages of precision and speed often outweigh the drawbacks. Industries need to remain adaptable to fully leverage this technology's potential.
This chart displays the average power output (in Watts) of different types of laser welding guns used in various applications.
Laser welding technology operates on a fundamental principle that harnesses the power of lasers to join materials. The process involves directing a focused beam of light onto the workpieces. This beam generates high temperatures, melting the material at the joint. The energy density of the laser allows for precision and minimal heat-affected zones, which is crucial in many applications. According to a report by the International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, laser welding can achieve welding speeds of up to 5 meters per minute, significantly enhancing productivity.
One key aspect of laser welding is its ability to work with various materials. Metals, plastics, and even some ceramics can be effectively welded. However, not all materials yield the same results. For instance, joining dissimilar metals often poses challenges, such as differing thermal expansion rates. A study by the Journal of Materials Processing Technology highlights that improper settings can lead to defects, such as lack of fusion and porosity. These factors make it essential for operators to understand their materials and the process to minimize errors and enhance weld quality.
While laser welding boasts numerous advantages, it is not without its limitations. Setup costs can be high, particularly for small businesses. Furthermore, the technology requires skilled personnel for operation and maintenance. A survey by the Laser Institute of America indicates that workforce training can be a significant hurdle for companies wanting to implement this technology. Addressing these challenges is necessary for maximizing the benefits of laser welding in modern manufacturing.
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Type | Type of laser used in the welding gun | Fiber Laser |
| Wavelength | Wavelength of the laser beam | 1060 nm |
| Power Output | Maximum output power of the laser | 1000 W |
| Cooling Method | How the laser gun is cooled | Water-Cooled |
| Welding Speed | Typical welding speed | 1-10 m/min |
| Materials | Common materials welded | Steel, Aluminum, Copper |
| Applications | Industries where laser welding is used | Automotive, Aerospace, Electronics |
A laser welding gun comprises several key components, each playing a vital role in its function. The laser source generates focused beams of light. This light produces intense heat, melting materials. A lens system is essential to direct and focus these beams accurately. The welding process depends heavily on proper alignment and adjustment of these components.
Cooling systems are also critical to prevent overheating. Lasers can generate immense heat. Without cooling, the equipment risks damage. Additionally, a control unit regulates the laser's intensity and duration. These features help maintain consistent weld quality. Users often overlook the importance of regular maintenance, which can lead to inefficiencies over time.
Tips: Always check the alignment before starting a weld. Misalignment causes weak spots. Also, keep the lens clean. A dirty lens can scatter the beam. This results in poor welding quality. Regularly evaluate the cooling system. An uninterrupted cooling process is crucial for optimal performance.
Laser welding technology is making waves in various industries. Its ability to create precise, strong welds with minimal heat input is crucial. This efficiency decreases the risk of thermally induced stress. In fact, recent reports show that laser welding can improve production speeds by up to 30%. This is vital in sectors like automotive and aerospace, where time is money.
The automotive industry, for instance, is increasingly adopting laser welding. A study indicates that over 60% of manufacturers are integrating this method into their production lines. With its capability for automation, laser welding reduces labor costs. Yet, companies do face challenges. Training staff to handle this technology requires investment and time. The learning curve can be steep. Some employees may struggle initially, causing delays.
Another application is in electronics manufacturing. The precision needed in soldering components is usually met with laser welding. It effectively joins components without damaging sensitive parts. However, maintaining the equipment can be demanding. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure consistent performance. Companies sometimes overlook this aspect, leading to unexpected downtimes.
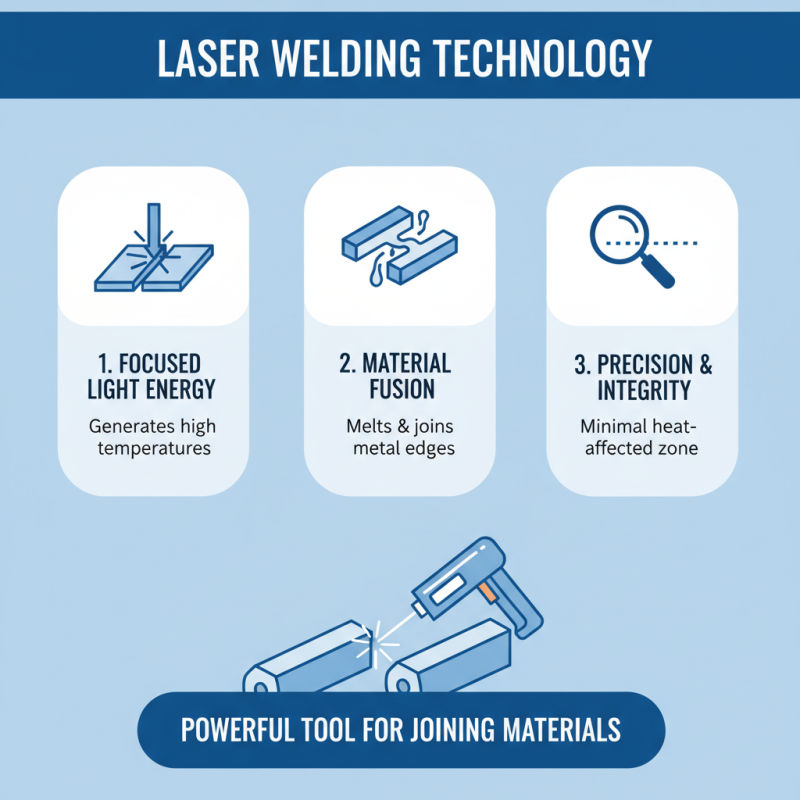
Laser welding guns are powerful tools for joining materials. They use focused light energy to create high temperatures. This process melts the edges of the metals, allowing them to fuse together. The precision of the laser ensures minimal heat-affected zones, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of sensitive components.
One clear advantage of laser welding is the ability to weld thin materials with ease. This makes it ideal for industries like aerospace and automotive. Additionally, laser welding is highly automated, improving efficiency. However, there are limitations to consider. The initial setup costs can be high, making it less accessible for small businesses. Furthermore, not all materials can be welded effectively with lasers. Certain alloys and materials may not yield strong bonds.
Heat management is another concern. While lasers minimize heat spread, improper settings can lead to warping. This necessitates skilled operators to calibrate the systems correctly. Reflection and absorption properties of materials can also affect the welding quality. These factors reveal the complexities involved. Each project may require a tailored approach to achieve the best results.






