1101 W. Sanilac Rd. Caro, MI 48723
989.673.6690
Laser etching is transforming industries. It combines precision and speed. According to a report by IBISWorld, the laser etching market is expected to grow by 8% annually over the next five years. This growth reflects its rising applications in various sectors, such as manufacturing, electronics, and consumer goods.
Expert Dr. Emily Tran, a leader in laser technology, states, “Laser etching enhances personalization in ways we never imagined.” This process uses focused laser beams to engrave intricate designs on materials. Its ability to create precise details makes it invaluable. However, there are challenges. One common issue is the risk of material damage if settings are incorrect. Understanding these nuances is essential for optimal results.
Despite its advantages, many still overlook the potential of laser etching. Businesses sometimes treat it as an afterthought rather than an integral part of their processes. Exploring this technology can lead to innovative solutions. It is crucial to reflect on how businesses can better integrate laser etching to fully harness its capabilities.
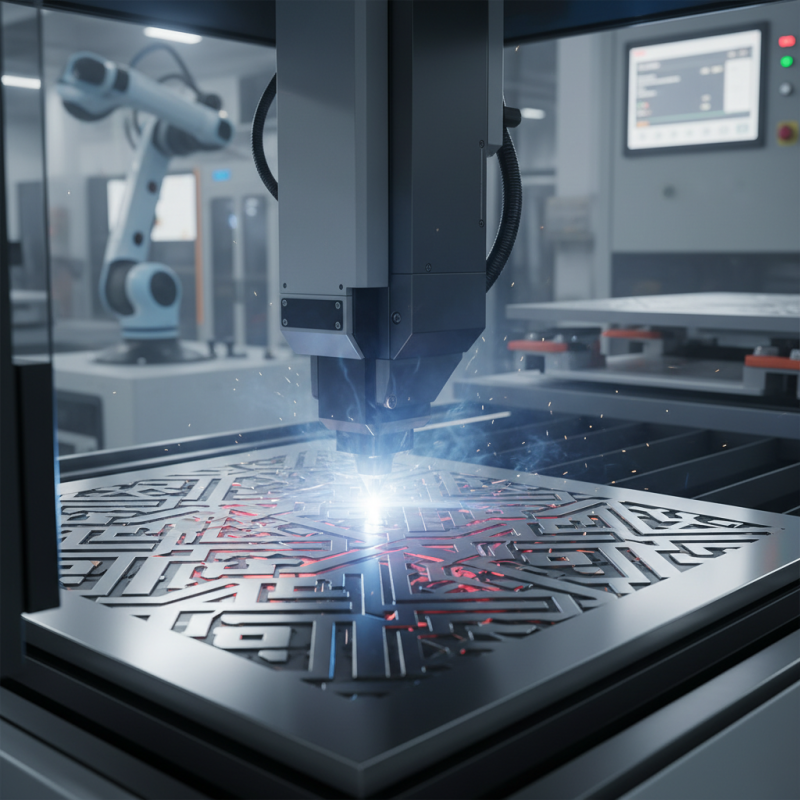

Laser etching is a precise method for marking materials using focused laser beams. This technique can engrave intricate designs on various substrates such as metal, wood, glass, and plastics. It's popular in numerous industries, ranging from automotive to jewelry manufacturing. The ability to create fine details makes laser etching highly desirable for branding and personalization.
One significant application of laser etching is in product labeling. Businesses use this method to etch logos or serial numbers directly onto products. This enhances durability and resistance to wear. Another fascinating use is in artistic creations. Artists often utilize laser etching to bring their visions to life on a variety of surfaces. However, the precision of laser etching requires careful planning and design.
There are challenges, too. The setting of the laser power and speed must be accurate. An incorrect setting may lead to unwanted results. Additionally, the etching process can create fumes and debris, which require adequate ventilation. Reflecting on these aspects can help users improve their techniques and results over time.
Laser etching is a fascinating process that combines precision and technology.
At its core, it utilizes focused laser beams to remove material from a surface. This method can work on various materials like wood, metal, and glass.
The laser creates heat, causing the material to vaporize or melt. The result is a permanent mark or design on the surface.
The principles behind laser technology in etching revolve around light absorption and material properties.
Different materials absorb laser energy differently. For instance, metals may require higher energy levels than wood or plastic.
Engineers need to adjust the laser’s speed and power based on these variables. However, achieving the right balance can be tricky.
Too much power can burn the material, while too little may result in incomplete etching.
Creating intricate designs can be challenging. Slight miscalculations in focus can shift the entire outcome.
Moreover, the cooling time after etching can affect quality. Some designs might not etch deeply enough, losing detail.
Observing these intricacies in laser etching is essential for improvement. Each project serves as a lesson,
highlighting the dance between technology and artistry.
Laser etching is a versatile technology used on various materials. Different surfaces yield unique results. Some materials shine brighter than others when etched.
Wood is a popular choice. It absorbs the laser well, creating sharp designs. The grain adds an appealing texture. However, results can vary based on the wood type.
Metal is another great option. Stainless steel and aluminum can be etched with precision. The contrast between etched and unetched areas is striking. Yet, it requires a specific skill to avoid over-etching, which can damage the surface.
Glass also works well, but it demands caution. The process can crack the glass if not carefully controlled.
Plastic is commonly used too. It allows for colorful designs that catch the eye. However, not all plastics are suitable. Some may emit harmful fumes when heated. This risk necessitates thorough research before proceeding.
In summary, selecting the right material is essential for successful laser etching. Each choice presents its own challenges and rewards.
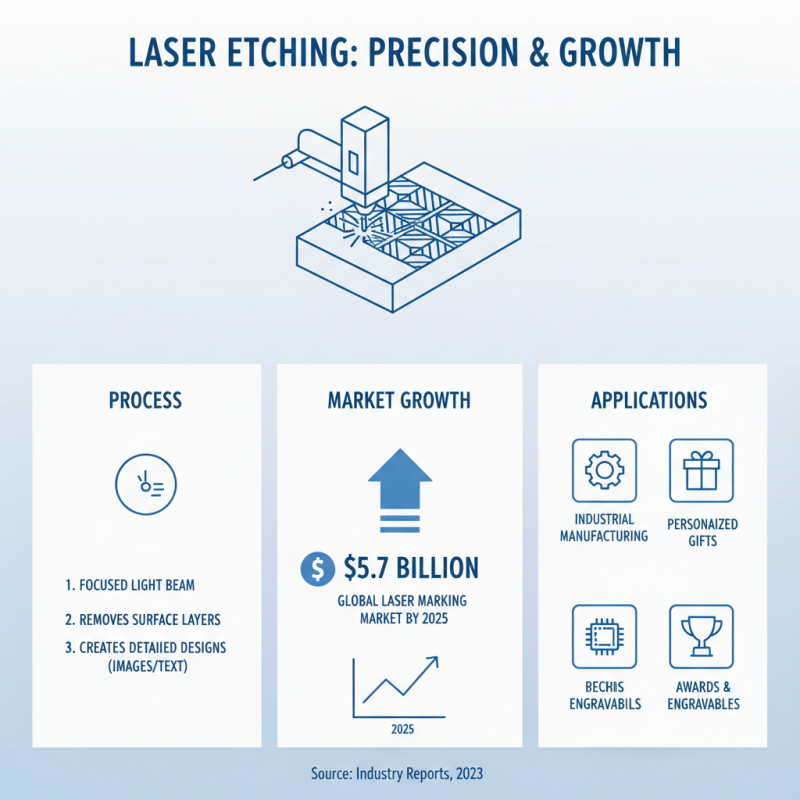
Laser etching is a precise and popular method for engraving designs onto various materials. The process involves using a focused beam of light to remove layers from the surface, creating detailed images or text. According to industry reports, the global laser marking market is expected to reach $5.7 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the increasing demand for laser etching in diverse applications, from industrial manufacturing to personalized gifts.
The step-by-step laser etching process begins with preparing the material surface. This often involves cleaning to ensure optimal adhesion and engraving quality. Next, a design is created using specialized software. The laser then precisely follows this design, scanning back and forth, often at high speeds. The etching depth can be adjusted for different effects, but this requires careful calibration. Data indicates that consistency is key, as even small variations can lead to suboptimal results. A recent study found that 15% of projects failed due to poor initial settings.
After etching, a thorough inspection is important. This step often reveals issues that may not be visible at first glance. Some etching jobs can show uneven results or surface inconsistencies. This necessitates a review of techniques used. Addressing these imperfections is crucial for ensuring high-quality output, which can significantly impact customer satisfaction and business reputation in today’s competitive market.
Laser etching is gaining traction in various industries due to its precision and versatility. One of its major advantages is the ability to create highly detailed designs on various materials. According to a recent industry report, the global laser engraving market is expected to reach $4.92 billion by 2026, driven largely by technological advancements and an increasing demand for customized products. The process uses focused laser beams to remove material layer by layer, resulting in intricate patterns and text.
However, laser etching does have limitations. The initial equipment cost can be steep, which may deter small businesses. Additionally, not all materials yield satisfactory results. For example, metals may require additional preparation and post-processing, complicating the workflow. Some operators may also overlook safety measures, as high-intensity lasers can pose risks if not handled correctly. This often leads to setbacks in project timelines and can compromise work quality.
In conclusion, while laser etching offers exciting possibilities, careful consideration is essential. Companies should weigh the benefits against the potential challenges. The need for skilled operators and the intricacies involved can present hurdles that require ongoing training and adjustments. Finding the right balance is key for successful implementation.






