1101 W. Sanilac Rd. Caro, MI 48723
989.673.6690
In the landscape of precision welding, the advent of advanced technologies has transformed traditional methodologies, making laser welders a compelling choice for manufacturers and craftsmen alike. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the laser welding market is projected to grow from USD 2.9 billion in 2020 to USD 4.0 billion by 2025, at a CAGR of 6.7%. This significant growth is driven by the increasing demand for high-quality welds and the superior capabilities that laser welders offer compared to conventional welding techniques.
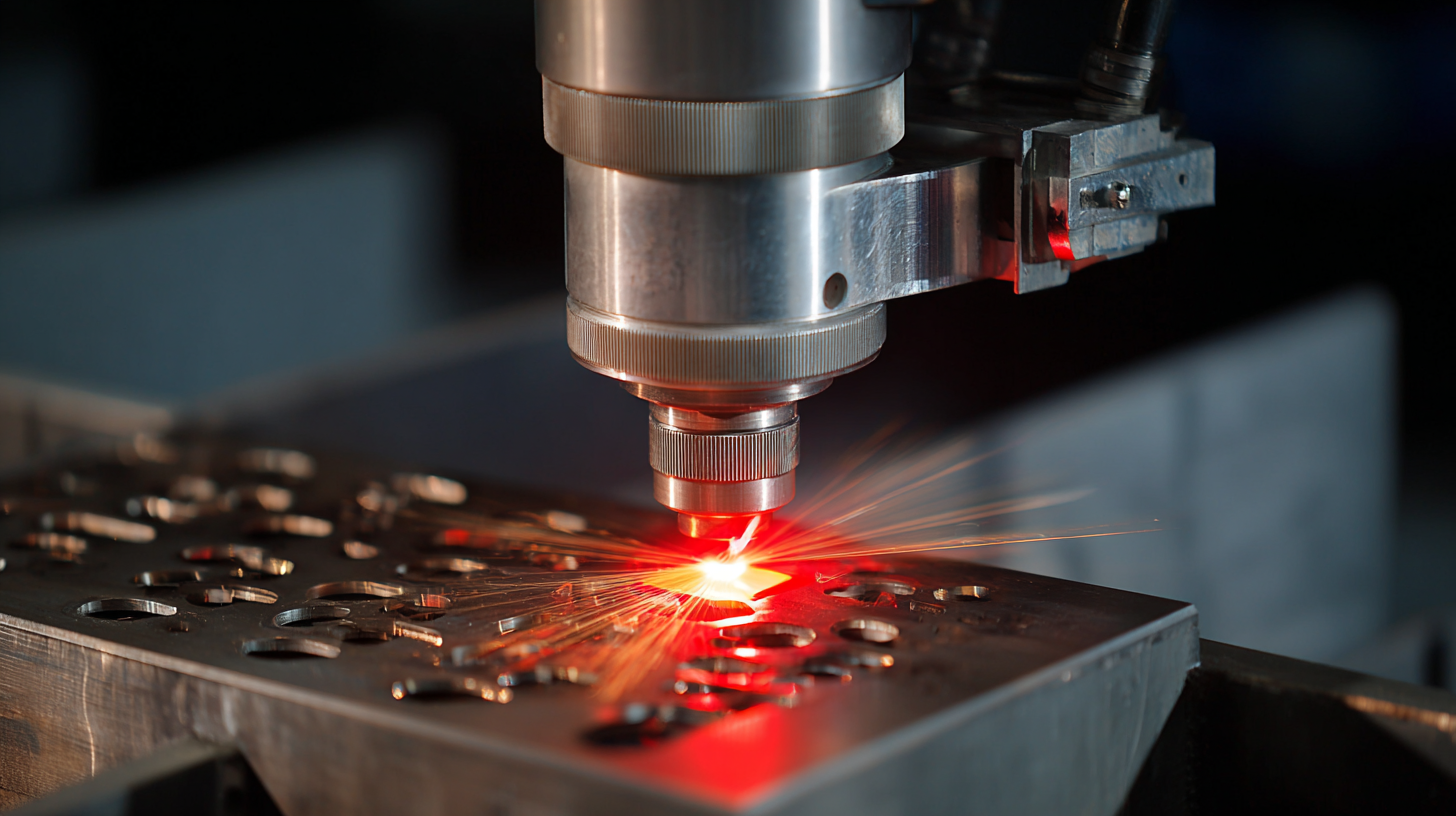

Laser welders provide exceptional precision and control, enabling the welding of intricate parts with minimal thermal distortion. The American Welding Society notes that laser welding can achieve welds as thin as 0.1 mm, a critical advantage in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics. Furthermore, laser welding processes are often more energy-efficient, reducing operational costs while enhancing productivity. As industries continue to prioritize efficiency and quality, the choice of laser welders emerges as an essential consideration for those seeking to meet evolving precision welding demands.
Laser welders have become increasingly popular in precision applications due to their numerous benefits. One of the most significant advantages is their ability to produce high-quality welds with minimal heat input. This characteristic reduces the risk of thermal distortion and warping, which is crucial when working with delicate components or materials that require strict tolerances. The focused energy of laser beams allows for precise targeting, which results in clean, strong joints that are essential for high-performance assemblies.
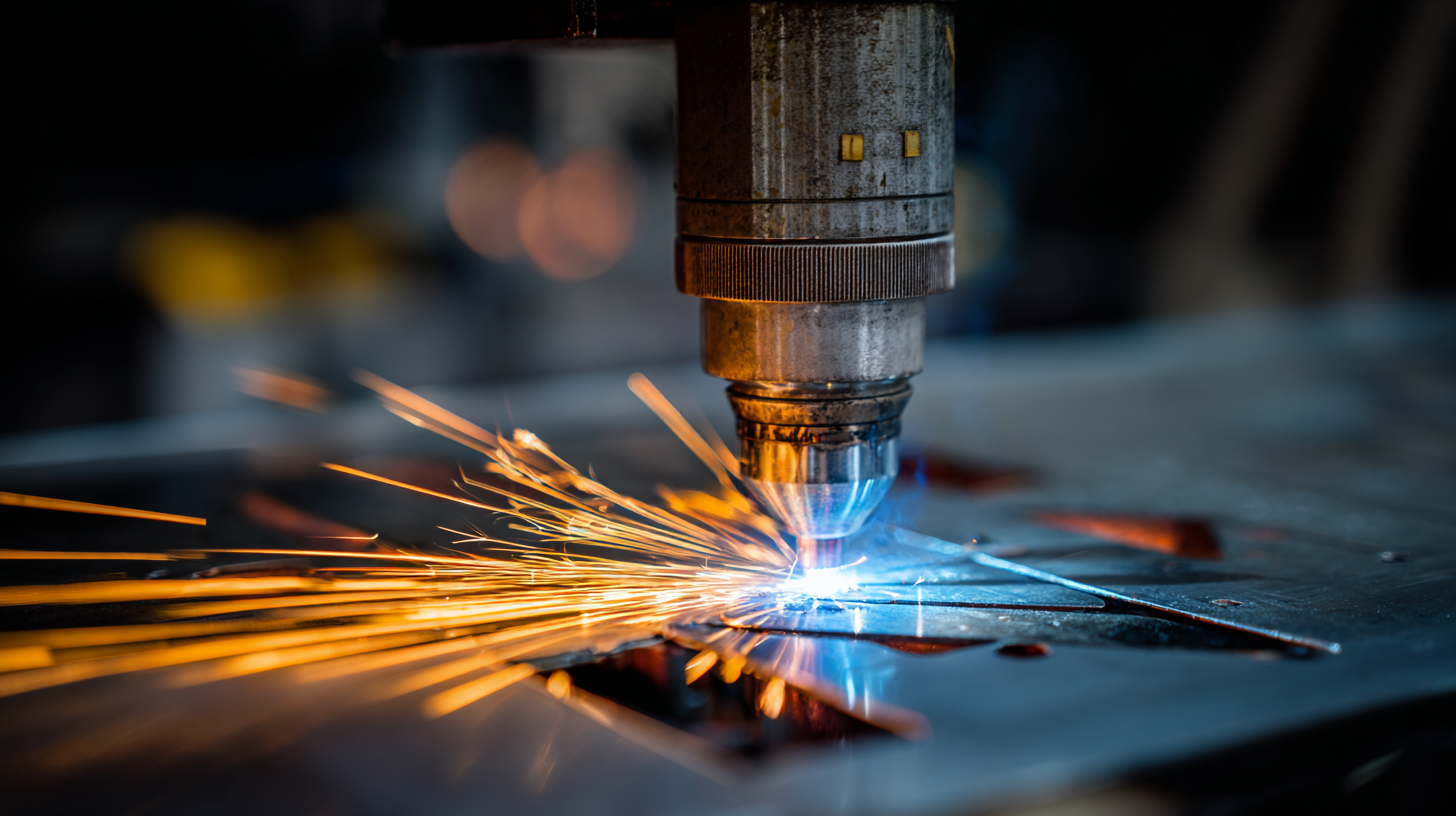

Additionally, laser welding offers exceptional speed and efficiency. The rapid melting and solidification process means that projects can be completed faster than traditional welding methods. This not only increases productivity but also minimizes downtime, making laser welders an ideal choice for industries that demand quick turnaround times. Furthermore, the technology is adaptable and can be used for various materials, including metals, plastics, and ceramics, widening its applicability across different sectors. This versatility, combined with its precision, solidifies laser welding as a superior option for meeting the rigorous standards required in precision welding tasks.
When it comes to precision welding, the choice of welding technology can significantly impact both the quality of the work and overall efficiency. Laser welding has emerged as a superior alternative to traditional methods such as MIG and TIG welding. According to a report by the International Institute of Welding, laser welding can increase welding speed by up to 70% compared to conventional techniques, making it an ideal choice for high-volume production environments. The precision of laser welding allows for narrower heat-affected zones, reducing the risk of distortion and ensuring a better end product.
Additionally, the versatility of laser welders stands out in industries that require intricate designs and minimal finishing work. For instance, laser welding excels in applications within the automotive and aerospace sectors, where components must meet stringent quality standards. A study published by the American Welding Society indicates that laser welding reduces post-weld processing time by approximately 30%, thus lowering overall production costs. This advantage, combined with the ability to weld dissimilar materials effectively, underscores why more manufacturers are transitioning to laser welding technologies for their precision welding needs.
When selecting a high-quality laser welder for precision welding needs, there are several key features to consider. First, look for advanced laser technology, such as fiber lasers, which have been shown to provide better efficiency and precision, with power savings of up to 80% compared to traditional welding methods according to a report by the International Institute of Welding. Additionally, consider the welder's energy output. A machine with adjustable power settings allows for versatility across different materials and thicknesses, enhancing the breadth of applications.
Another crucial feature is the control software. Advanced welding machines come equipped with programmable settings and real-time monitoring capabilities. This not only improves consistency and repeatability in weld quality but also reduces defects, as noted in a study published by the Welding Research Council, which highlighted that automated systems can decrease error rates by up to 40%.
Tip: When evaluating laser welders, prioritize those with enhanced cooling systems. Effective thermal management prevents overheating, which is essential for maintaining precision during prolonged use.
Tip: Always test the welder with the specific materials you plan to work with. Different materials react uniquely to laser welding, and hands-on trials can reveal the machine's true capabilities.
Laser welding technology has made significant inroads into various industries, owing to its precision and efficiency. Sectors such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices are among those that greatly benefit from adopting laser welding. This advanced technique allows manufacturers to achieve tighter tolerances and higher-quality welds, which is essential in producing complex components that require durability and reliability.
For instance, in the automotive sector, laser welders enable the assembly of lightweight materials, contributing to fuel-efficient designs and overall vehicle performance. In aerospace applications, precision welding is vital for ensuring safety and compliance with stringent industry regulations. The medical device industry also relies on laser welding for its ability to create sterile and intricate components essential for advanced healthcare solutions.
**Tips:** When considering laser welding for your manufacturing processes, ensure that you assess the specific requirements of your projects. Understanding the types of materials and designs you will be working with can help you choose the right laser welder. Furthermore, investing in skilled operators who are trained in laser technology can enhance the effectiveness of your welding processes, leading to better production outcomes and reduced waste.
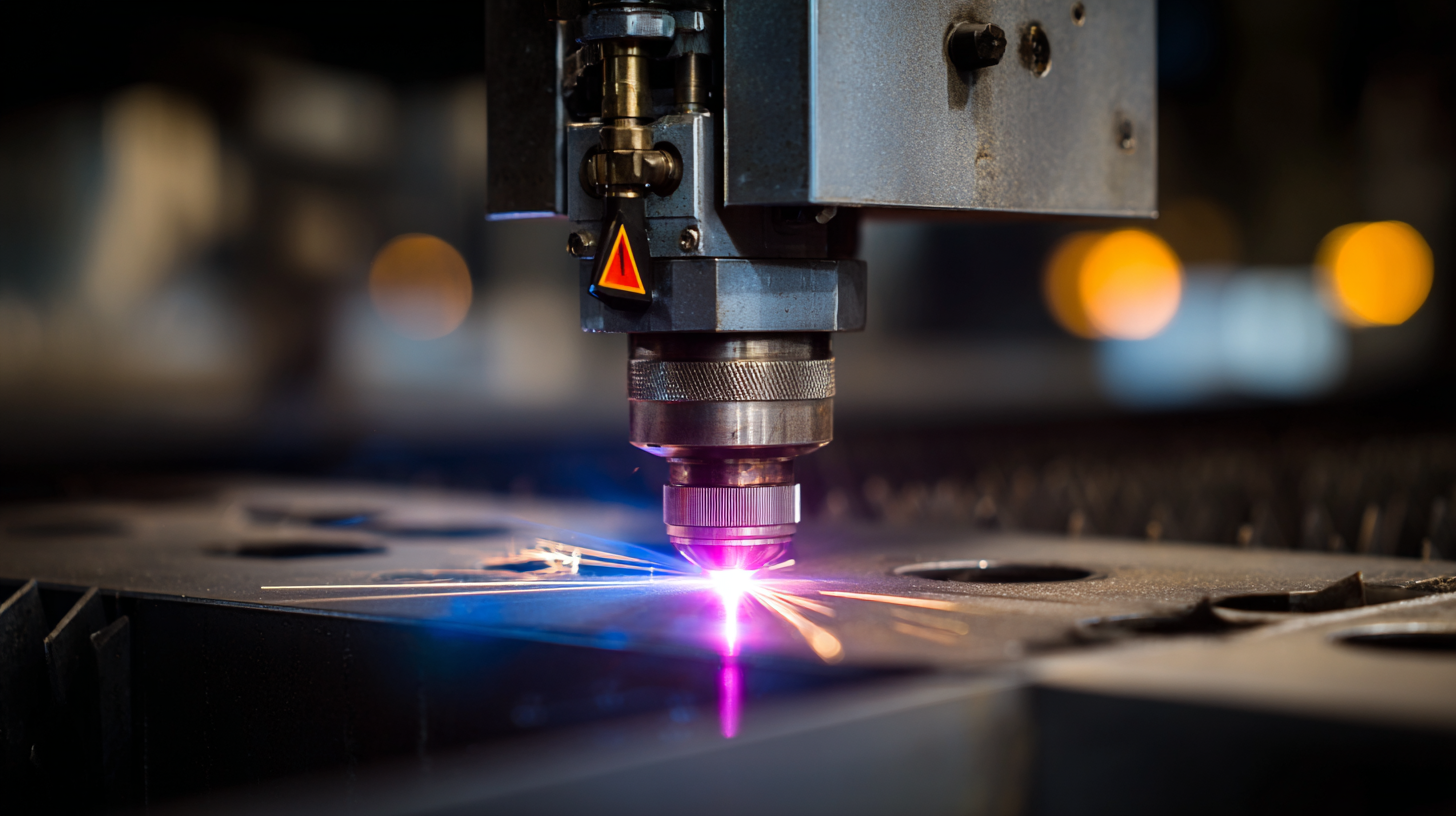

When considering precision welding, laser welders present a cost-effective solution with significant long-term savings. According to industry reports, laser welding technology can reduce material waste by up to 30%, which directly translates to lower costs in material purchasing and disposal. Moreover, the energy efficiency of laser welders contributes to reduced operational expenses, as they utilize focused laser beams that require less power compared to traditional welding methods. This efficiency not only cuts costs but also enhances the overall productivity of welding operations.
Additionally, the durability and longevity of laser welders should not be overlooked. As companies increasingly invest in modular construction, the demand for robust and reliable welding equipment is on the rise. Laser welders are known for producing high-quality, precise welds that minimize the need for rework, further driving down costs over time. According to recent studies, businesses that adopt laser welding technologies report reduced project timelines due to faster weld speeds and less post-weld processing, making them an ideal choice for modern manufacturing environments. Such advantages ensure that choosing a laser welder is not only a financially sound decision but one that aligns with the industry's push towards innovation and sustainability.
| Feature | Traditional Welding | Laser Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Lower Initial Equipment Cost | Higher Initial Equipment Cost |
| Operational Cost | Higher Energy Consumption | Lower Energy Consumption |
| Material Waste | Higher Material Waste | Minimal Material Waste |
| Welding Speed | Moderate Speed | High Speed |
| Precision | Moderate Precision | High Precision |
| Maintenance | Frequent Calibration Required | Lower Maintenance Needs |
| Training Requirements | Basic Skillset | Specialized Training Required |
| Long-Term Savings | Lower Savings | Higher Savings Over Time |